Lab Introduction
It is undeniable that during a learning process it would be helpful if we could deal with the examples of real-life challenges in order to commit to memory and put them into practice. For practicing in the realm of data transmission network. They help to simulate and emulate the traffic flow, configurations, related procedures and the behavior of network protocols which we are facing in the field. The lab environments help to figure out the connected concepts and decrypt how to accomplish. There are 3 well-known solutions in which we can warp up the subjects.
How to propose GNS3?
Here we are going to shed some light on a marvelous simulator called Graphical Network Simulator-3 provide you a platform to emulate complex network designs on real routers, switches, firewalls and vast majority of network devices such as Cisco routers and switches. GNS3 is a software which is released under an open-source license. You are able to run real Cisco IOS images using Dynamips in the GNS3 infrastructure, designing complicated network on your personal computer and studding in more details. Dynamips (MIPS Processor Emulation Program) enables network devices such as Cisco Routers, Juniper, MikroTik and Vyatta to execute in a virtual environment.
How does GNS3 gain qualification in emulating IT infrastructure?
GNS3 is evolved to emulate, configure, test and troubleshoot virtual an real networks by supporting many devices from multiple network vendors including Cisco Virtual Routers and Switches, Cisco ASAs, Brocade vRouters, Cumulus Linux switches, Docker instances, HPE VSRs, multiple Linux appliances and many others. By giving an advantage of GNS3 you can check interoperability between many vendors and even testing setups using network technologies with SDN, NFV, Linux and Docker. GNS3 uses IDLE-PC value to show better performance of Cisco Routers or Switches IOS. You can configure the Idle-PC value when adding a device to the program.
GNS3 software components!
- The GNS3-all-in-one software (GUI)
- The GNS3 virtual machine (VM)
Network Simulation Terminology
emulator (hypervisor) that was written to emulate Cisco IOS.
Dynagen is a front-end for managing dynamips. It controls dynamips, much in the same way that virsh/libvirtd controls KVM.
Free Cisco PIX Firewall Emulator based on QEMU
Packet Capture Utility, Driver for Sniffer
Network Protocol Analyzer
Virtual PC Simulator a light-load PC simulator in which runs Windows or Linux that allows you to use VPCS on your GNS3 project’s network diagram to verify network connectivity such as pings, traceroute and DHCP.
a compute resource that uses software instead of a physical computer to run programs and deploy apps.
the same as VMware but is released under an open-source license
IOU is IOS on Unix (Solaris, if you want to be specific). It’s a version of IOS compiled to run on workstations.
Feature sets and benefits
- Fully free and Open-Source
- No limit on the number of devices supported (CPU and RAM are your curtailment)
- GNS3 supports all VIRL images (IOSv, IOSvL2, IOS-XRv, CSR1000v, NX-OSv, ASAv)
- Supporting Multi-vendor environment
- To run without hypervisor and run with both free and paid hypervisors; Virtualbox, VMware Workstation, VMware Player, ESXi, Fusion
- GNS3 has native support for Linux without the need for need for additional virtualization software
Image Licensing
You can download IOS images from Cisco.com and purchase a VIRL license.
GNS3 installation package
GNS3 installation package contains several additional tools and components. The following table provides a brief description of these tools.
WinPCAP
Npcap
Wireshark
Dynamips
QEMU
VPCS
WinPCAP
This component connects GNS3 to the host computer’s network. It allows the nodes that are simulated on GNS3 to communicate with nodes that available on the host computer’s network.
Npcap
This component is the replacement of WinPCAP. Based on the version of Windows, select either Npcap or WinPCAP. If you are installing GNS3 on Windows 10, select Npcap. If you are installing GNS3 on a previous version of Windows, select WinPCAP.
Wireshark
This component is used to capture and view data packets exchanged between nodes.
Dynamips
This component is used to run GNS3 from the host system.
QEMU
This component is used to create a virtual computer and to run GNS3 from that virtual computer. If you want to run GNS3 from a virtual computer, you should use GNS3VM instead of this component.
VPCS
This component is used to create a lightweight virtual PC that supports basic testing and troubleshooting commands such as ping and traceroute.
cpulimit
GNS3
TightVNC
Solar-Putty
Virt-viewer
HAXM
cpulimit
This component is an add-on to the QEMU component. It is used to limit QEMU using 100% CPU of the host computer.
GNS3
This is the core component of GNS3. It installs and runs GNS3 on the computer.
TightVNC
This is a VNC client. It is used to connect to appliance graphical user interfaces.
Solar-Putty
This is the default console application of GNS3.
Virt-viewer
This is an add-on component of QEMU. It provides an alternative display of QEMU desktop.
HAXM
This component is used for hardware acceleration. This component is available only if the host system uses Intel CPU.
Two ways of installing the latest release of GNS3 on Ubuntu 22.04
- Install from apt repository (Packages)
- Installing from source
Installing from source
First if you decide installing GNS3 from source, use the Github procedure,
https://github.com/GNS3/gns3-server
Install from apt repository (Packages)
Let’s concentrate on the installing procedure of GNS3 from apt repo. Our effort is to show that the instructions on Ubuntu-based distributions (64-bit only) such as Ubuntu 22.04, Linux Mint.
GNS3 packages are available on a GNS3 PPA repository, first, add the repository by running the commands below:
! PPAs are Personal Package Archives in which there are software repositories designed for Ubuntu users, allows them to create their own repositories to distribute software.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gns3/ppa
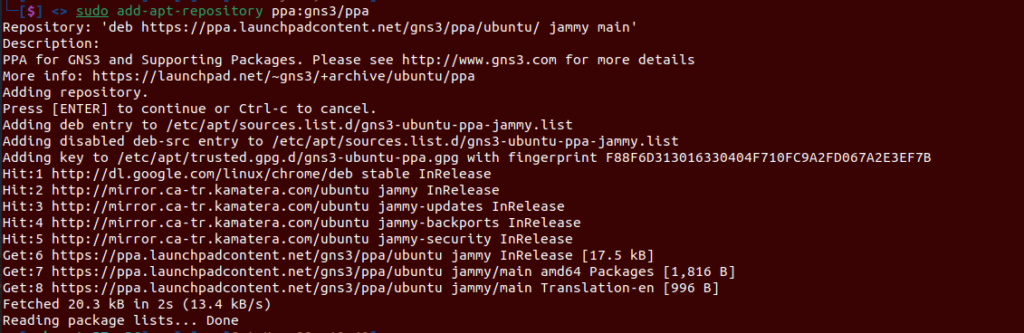
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install gns3-server gns3-gui
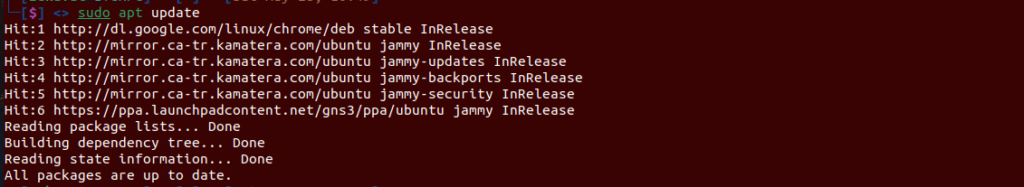
There will be an installation of a lot of packages and GNS3 dependencies.
Previous
Next
IOS on Unix
It is a miracle, let me see what do we have more around IOU,
IOU is IOS on Unix (Solaris, if you want to be specific). It’s a version of IOS compiled to run on workstations. It’s faster and lighter than emulation. Cisco transitioned to IOL images, which are x86-64 compatible versions of IOS that natively run in Linux. Since everyone and their kid brother still refers to IOL images as “IOU”.
License
You will need a license for your GNS3 VM to run IOU. This license is provided by Cisco. GNS3 called this license file iourc.
Please note that GNS3 cannot provide you images or licenses.
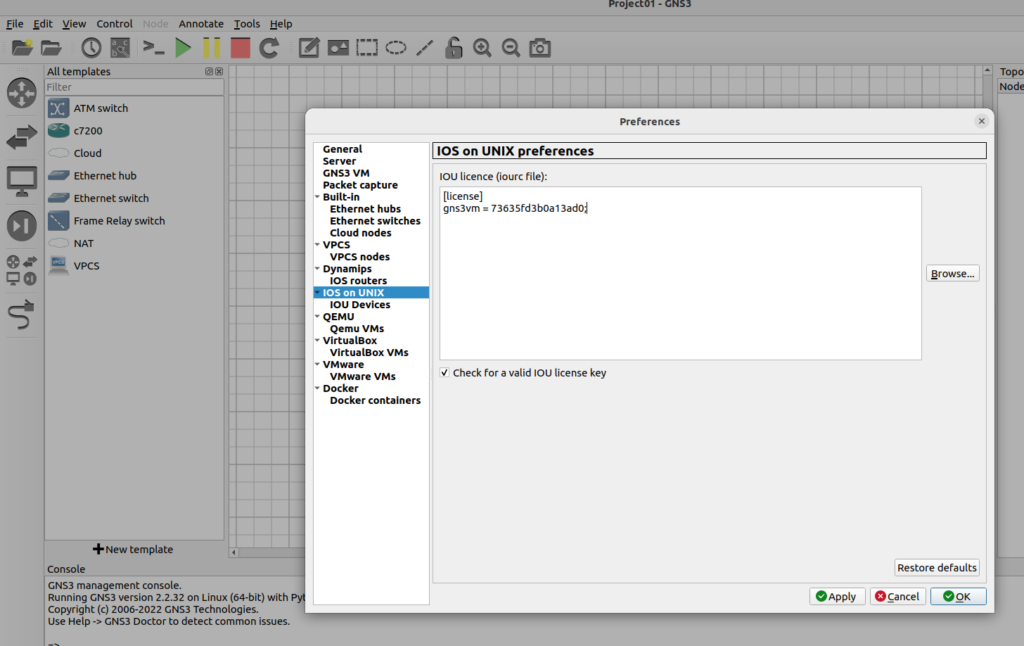
The content of the license file will be like this:
[license]
gns3vm = 42aa42bb42cc84ff;
GNS3 – Add Support for IOU (Optional)
If you want IOU support
You would find out the way to allow GNS3 backs IOS on Unix (IOU), you’ll have to enable running of x86 packages in a 64-bit system.
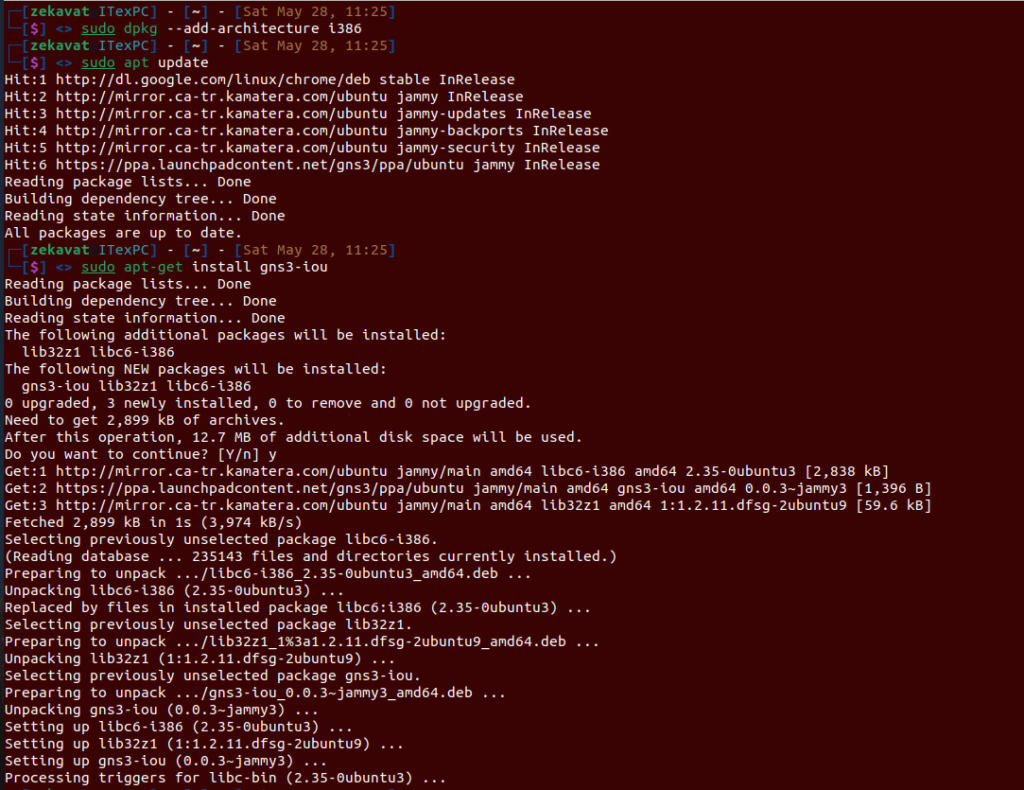
sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386
sudo apt update
Once it is activated, install related package.
sudo apt install gns3-iou
GNS3 VM
Since IOU images can be run in Linux, you will need to use a Linux VM to use it when running GNS3. For Windows/Mac OSX users, the GNS3 VM is available. Use of the GNS3 VM is optional for users running GNS3 natively in Linux.
Download the source of GNS3 vm for virtualization platform you are dealing with.
https://www.gns3.com/software/download-vm

If you want to use IOSvL2, IOU, IOSv, IOS-XRv, ASAv or want to create more complex topologies, the GNS3 VM is recommended for Windows and Mac OS implementations (it’s optional for Linux users).
It is going to elaborate the import of the GNS3 VM for VMware but instructions for VirtualBox are similar. You can perceive the better option of virtualization environment would be VMware because it’s faster and supports nested virtualization (the VMs inside the VM are accelerated by your CPU).
GNS3 supports both VMware Workstation Pro and VMware Fusion (Paid software), as well as VMware Player (Free software) and VMware ESXi. VMware Player requires the installation of additional free software (VMware VIX).
https://wiki.vi-toolkit.com/index.php?title=VIX
Extract the downloaded .zip archive
7z x GNS3.VM.VMware.Workstation.zip
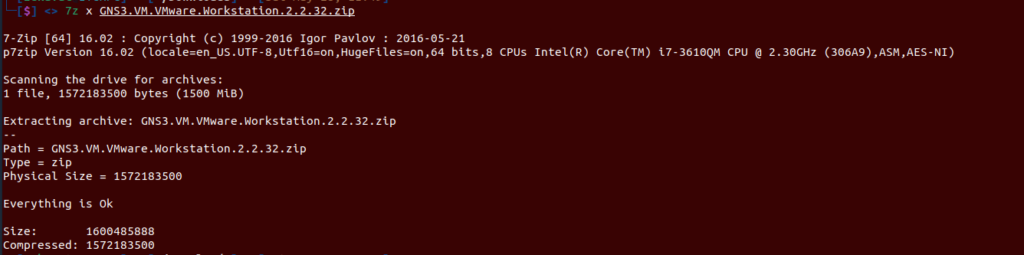
This extracts the “GNS3 VM.ova” file stored within the compressed archive, in order to import it into VMware Workstation.
In VMware Workstation, click ‘Open a Virtual Machine’ Navigate to the directory where the extracted GNS3 VM.ova is located, and click ‘Open’ to open the OVA, Leave the virtual machine name as ‘GNS3 VM’, and click ‘Import’ VMware Workstation will import the GNS3 VM
Previous
Next
The GNS3 VM will show as available in VMware Workstation. Leave all settings at their defaults. You have imported the GNS3 VM for taking advantage of IOU and more resource management.
For the warning message of KVM support is not available please be sure that it has been enabled in your system BIOS/UEFI.
For Windows and Mac OSX users, running appliances on your local computer will limit you to only running certain devices, like the legacy IOS images that Dynamips supports (see here), VPCS, and the other devices that GNS3 includes in the base installation (like VPCS, the built-in hub and ethernet switches, etc…)
This is not the case with users running GNS3 in Linux. GNS3 can run IOS images, QEMU/KVM VMs, and Docker containers natively, so they should select the local server optional, unless they are optionally using the GNS3 VM instead.
Now, we are going to present the GNS3 VM to the GNS3 environment,
Click ‘edit’ open ‘Preferences’, go ‘GNS3 VM’ select the checkbox of ‘Enable the GNS3 VM’, choose the virtualization engine you’re using, in the settings area, pick out the vm name of your virtual machine in the VMware Workstation.
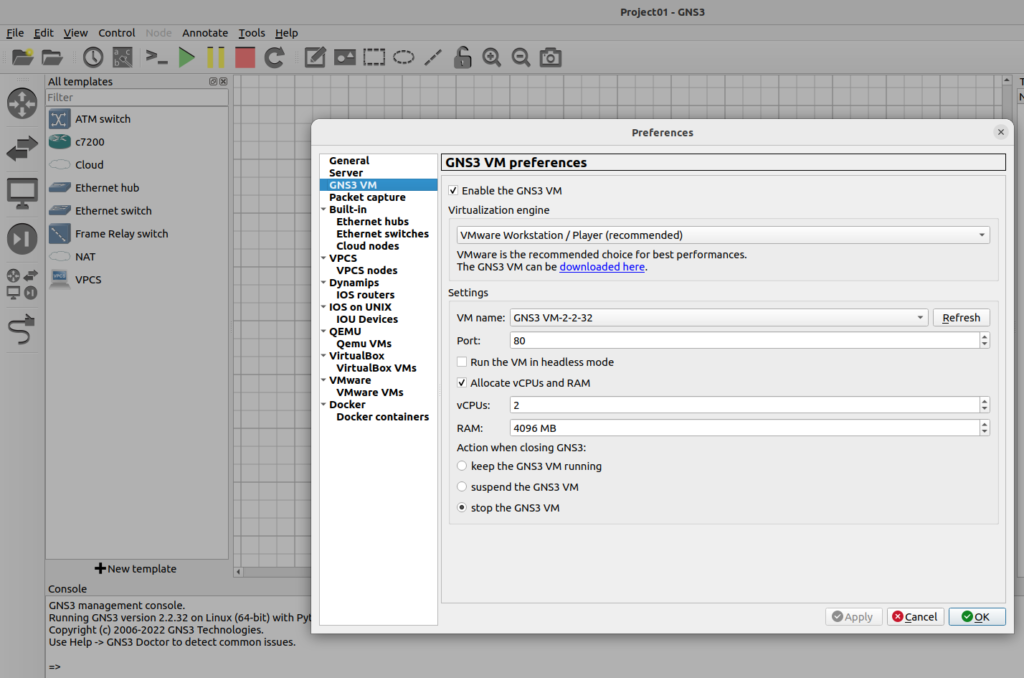
let’s imagine a situation that sometimes happen, if you run the GNS3 and see the GNS3 VM is properly running, green mode view in the server summary docks, but GNS3 doctor reflect an issue in the log console says that ‘GNS3 VM is not on the same network as the local server, apparently this is a limitation in the current code the GNS guys are working on fixing it, however you can solve it by changing the host binding picking out the IP address of your system’s network interface;
Edit –> Preferences –> Server –> “Host binding” drop-down menu
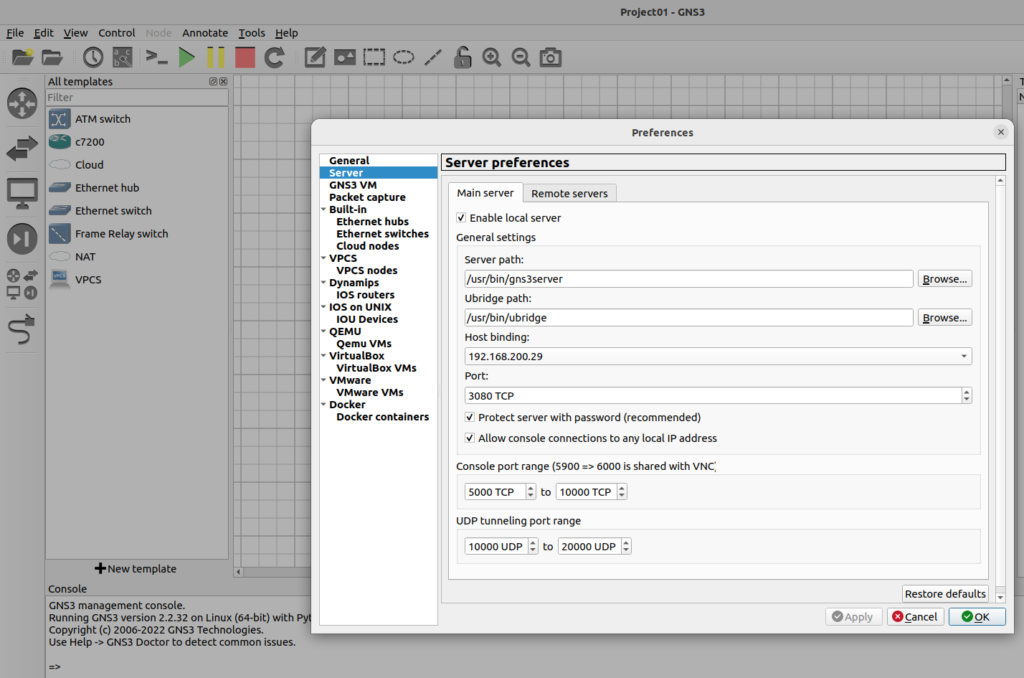
Next time running the GNS3, GNS3 VM booted successfully and linked to the GNS3, the IP address of the GNS3 VM will be displayed.
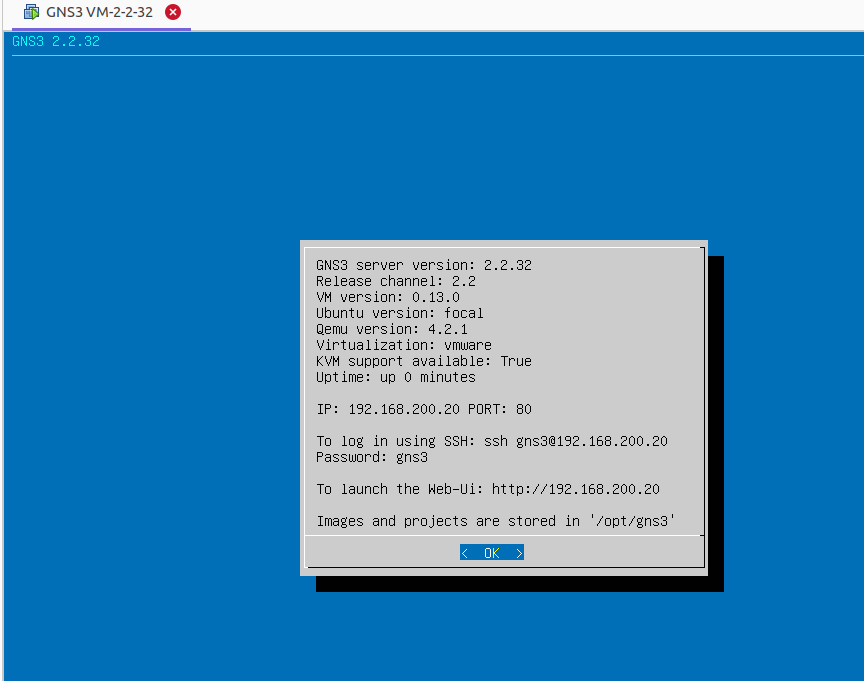
Adding IOU Devices
Now it’s time to configure IOU, definitely you recall that we talked about IOU licensing, you have to purchase ‘iourc’ from Cisco.
A license isn’t required to use IOS images with GNS3. A license IS required for IOU, I don’t know of any way to get one outside of working for Cisco, or being part of very specific training. Pretty much everyone uses the IOU license generator, or bypasses IOU and uses vIOS images from VIRL instead.
Generate Cisco IOURC license key on GNS3 VM using Python 3
Connect through SSH to the GNS3 VM;
Ssh gns3@192.168.200.20
Password is gns3, then for accessing the shell of your virtual machine, choose ‘shell’ to open a console.
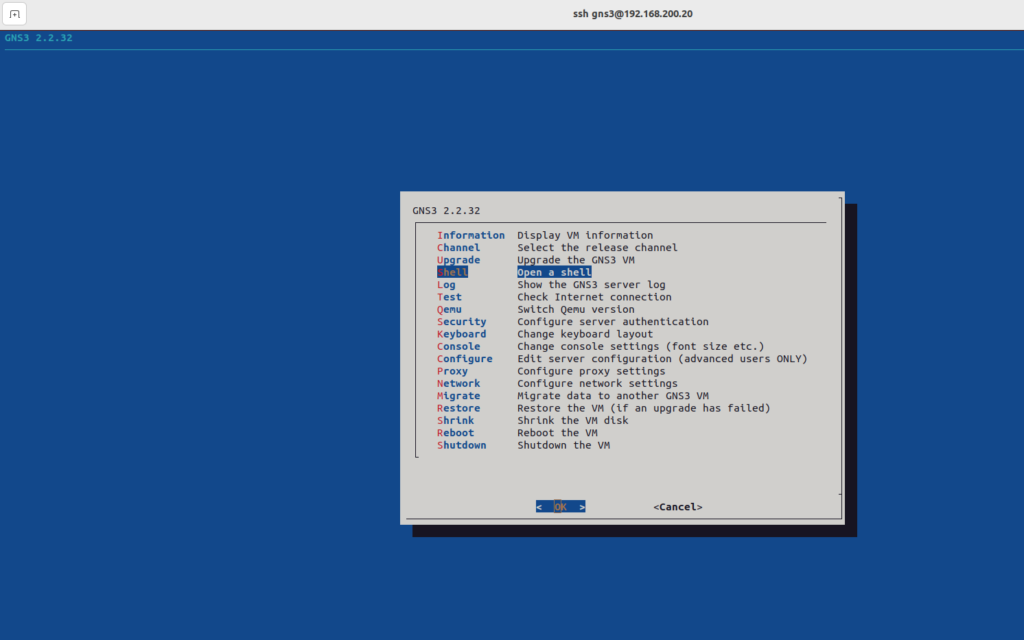
Download the Keygen using the following command;
wget http://www.ipvanquish.com/download/CiscoIOUKeygen3f.py
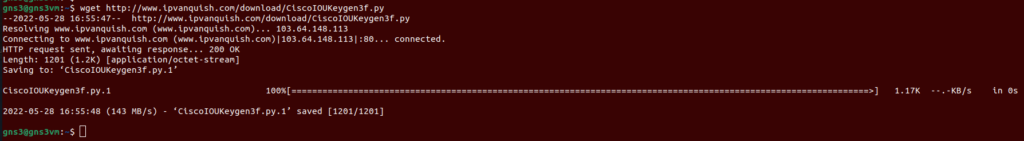
After downloading the code, compile it by using the below command;
python3 CiscoIOUKeygen3f.py

After compiling a Python file, a file called iourc.txt will be created;
Cat iourc.txt
Copy and paste the license key in the file to the Preference> IOS on the UNIX section of GNS3;
Next step is to provide Cisco IOU L2 and Cisco IOU L3, go to the GNS3 marketplace > appliances;
https://www.gns3.com/marketplace/appliances
What do we do for having IOU devices?
Download the files for one of the supported version listed below, Cisco IOS on UNIX Layer 2 and 3 image,
Setup IOU, Licensing and adding images,
Import the. gns3a file in GNS3.
Cisco IOU L2, Versions Supported
Cisco IOU L2 15.1g
Cisco IOU L2 15.1a
Cisco IOU L2 15.2d
Cisco IOU L2 15.1g
File name: i86bi-linux-l2-ipbasek9-15.1g.bin
MD5: 0b8b9e14ca99b68c654e44c4296857ba
Size: 62 MB
Cisco IOU L2 15.1a
File name: i86bi-linux-l2-adventerprisek9-15.1a.bin
MD5: 9549a20a7391fb849da32caa77a0d254
Size: 73 MB
Cisco IOU L2 15.2d
File name: i86bi-linux-l2-adventerprisek9-15.2d.bin
MD5: f16db44433beb3e8c828db5ddad1de8a
Size: 105MB
Cisco IOU L3, Versions Supported
Cisco IOU L3 155-2T
Cisco IOU L3 15.4.1T
Cisco IOU L3 155-2T
File name: i86bi-linux-l3-adventerprisek9-ms.155-2.T.bin
MD5: 45e99761a95cbd3ee3924ecf0f3d89e5
Size: 173 MB
Cisco IOU L3 15.4.1T
File name: i86bi-linux-l3-adventerprisek9-15.4.1T.bin
MD5: 2eabae17778316c49cbc80e8e81262f9
Size: 153 MB

1 Comment